NBCT Common Data Model (CDM): Integrating and Harmonizing Electronic Health Records across Hospitals
Mission
The National Biobank Consortium of Taiwan (NBCT) is dedicated to advancing biomedical research by constructing a standardized Common Data Model (CDM) to support precision medicine research. This initiative focuses on three core missions:
- to assemble a model of common data elements with sufficient information for patient disease diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up prognosis information,
- to facilitate data interoperability for patient care and research,
- to maintain sufficient data quality.
Overview
The NBCT CDM project supports hospitals in establishing standardized medical data repositories, enabling the effective reuse of clinical information stored in electronic health records (EHRs) and disease registries.
As illustrated in Figure 1, the hospital’s IT team extracts relevant data, such as electronic medical records and Taiwan Cancer Registry entries, from the institution’s biobank systems (①). These datasets are processed locally using NBCT-provided software, ensuring compliance with the Human Biobank Management Act.
After data transformation and de-identification, information is securely stored on offline computers within the biobank (②). The system then categorizes the data into thematic datasets (e.g., breast cancer, colorectal cancer) for streamlined analysis (③).
Before being shared with approved researchers, the data undergoes aggregation and secondary encryption using a unique coded identifier (④). These de-identified datasets are then distributed to eligible applicants through a secure delivery system (⑤).
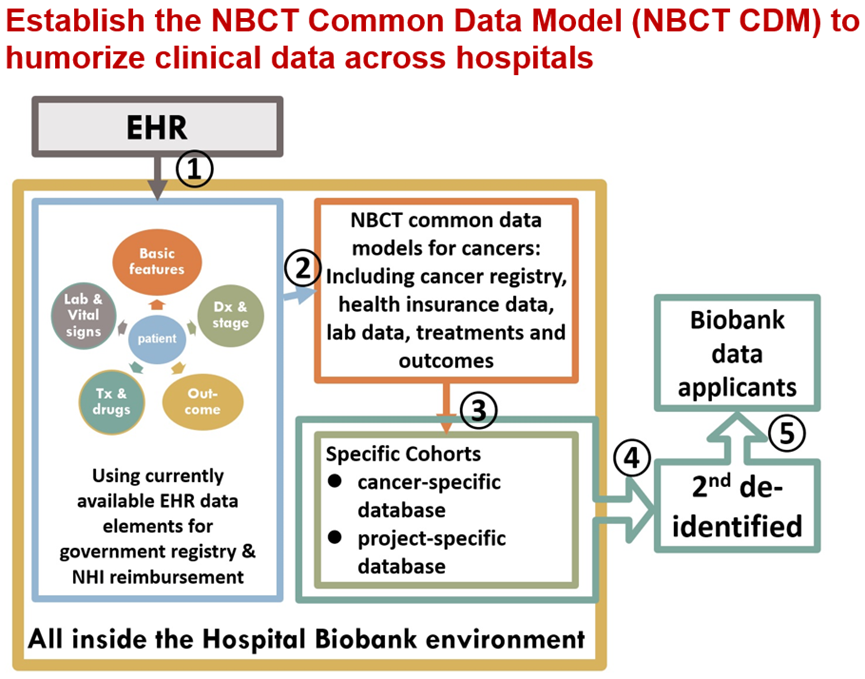
Figure 1: Establish the NBCT Common Data Model (NBCT CDM) to humorize clinical data across hospitals
Data Standardization and Sources
In the initial phase, the CDM focuses on structured clinical data fields (Figure 2), prioritized for their interoperability and standardization potential.
Primary data sources include the routine submission formats required by the National Health Insurance Administration (NHIA) for outpatient, inpatient, and laboratory examination data and data submitted to the Health Promotion Administration (HPA) for the Taiwan Cancer Registry. These standards ensure consistency with national healthcare data policies and improve cross-hospital comparability.

Figure 2: Clinical Medical Data
Distributed Platform for Secure Data Access
NBCT has developed a distributed data delivery system that connects central and local biobank platforms (Figure 3). Through this system, qualified researchers can apply for access to harmonized clinical datasets via a secure application and review process.
The NBCT Central Office coordinates with individual biobanks to manage data requests, ensuring all shared data remains de-identified, encrypted, and compliant with regulatory and ethical standards (Figure 4).

Figure 3: NBCT Distributed System

Figure 4: NBCT Central office working with biobanks
Social Value and Future Outlook
By building a robust and interoperable Common Data Model, NBCT strengthens Taiwan’s capacity for precision medicine, population health research, and real-world evidence generation. This initiative enhances the utility of biobanks, fosters cross-institutional collaboration, and ultimately contributes to improved healthcare outcomes for all.